CV_learning_notes(1)
Basic Concepts in Computer Vision
Camera
- Pinhole camera
-
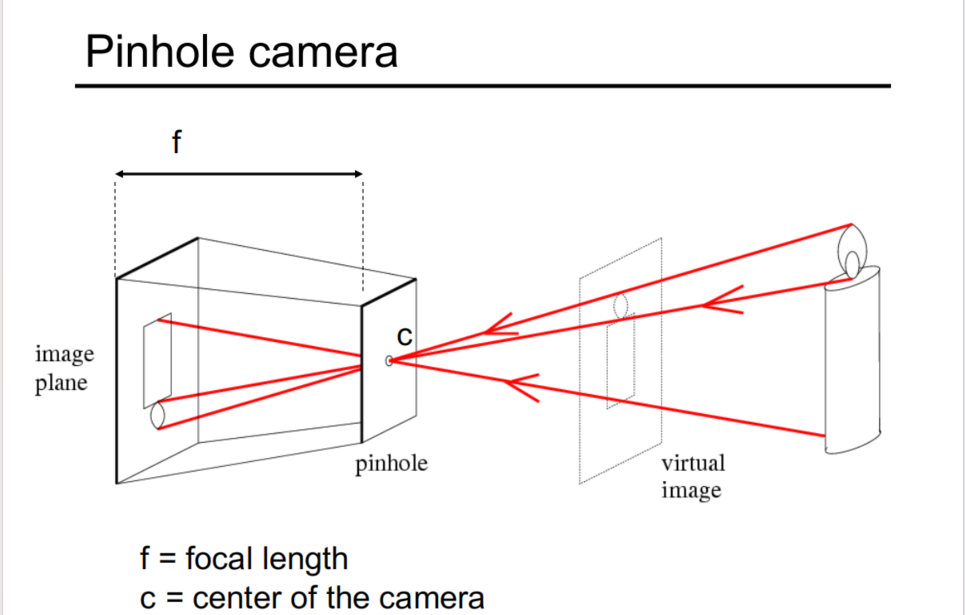
-
在投影过程中丢失了较多的信息
- length(相似三角形)
- angles(直观来看)
-
尽管直线得以保留但也引入了
vanishing points- 定义
- All parallel lines converge to a vanishing point
- Each direction in space is associated with its own vanishing point
- Exception: directions parallel to the image plane
- 特性
- 平行的3D线投影相交在Vanishing points
- 平行的3D面投影相交在Vanishing line
- 但相交并不一定平行
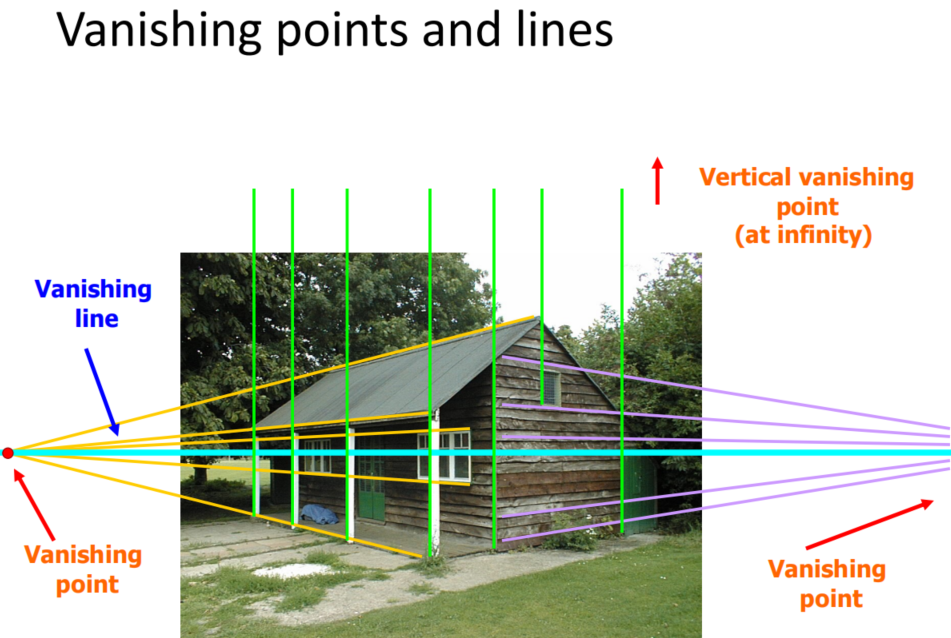
- 定义
-
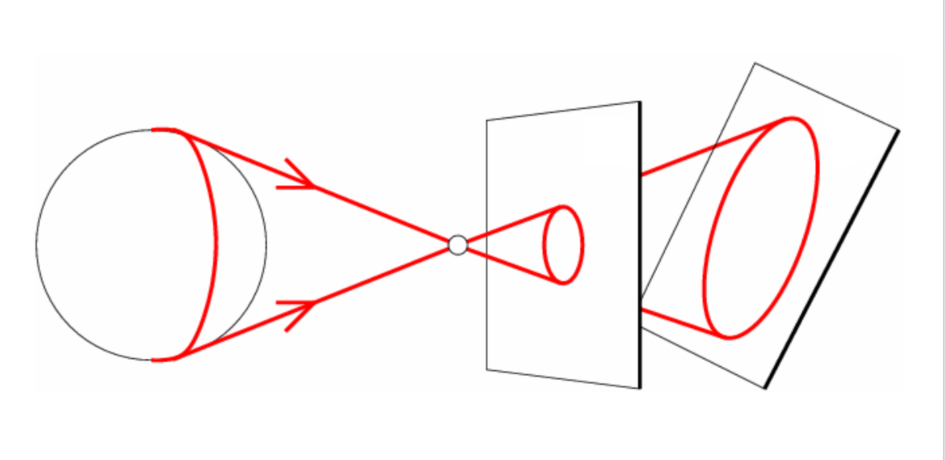
Perspective distortion
- 由于image plane切的问题,而并非视觉的幻想或是镜头的缺陷
-
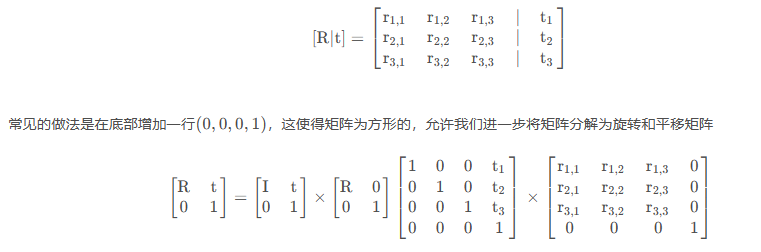
齐次坐标系
- 使在投影空间中进行图形和几何计算成为可能
- 通过利用齐次坐标就可以表示无穷远处的点。
- 把齐次坐标转化为笛卡尔坐标的方法是前面n-1个坐标分量分别除以最后一个分量即可
-
相机矩阵
- 相机外参:世界坐标系到相机坐标系
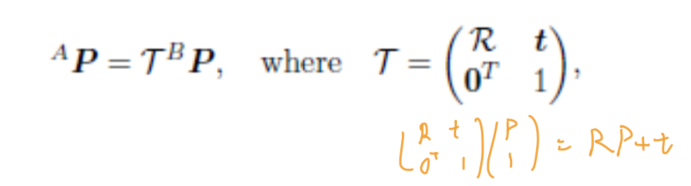
- 其中是相机坐标系,世界坐标系
R表示旋转矩阵,t表示平移向量- 决定了相机的位姿
- 相机内参:相机坐标系到像素坐标系
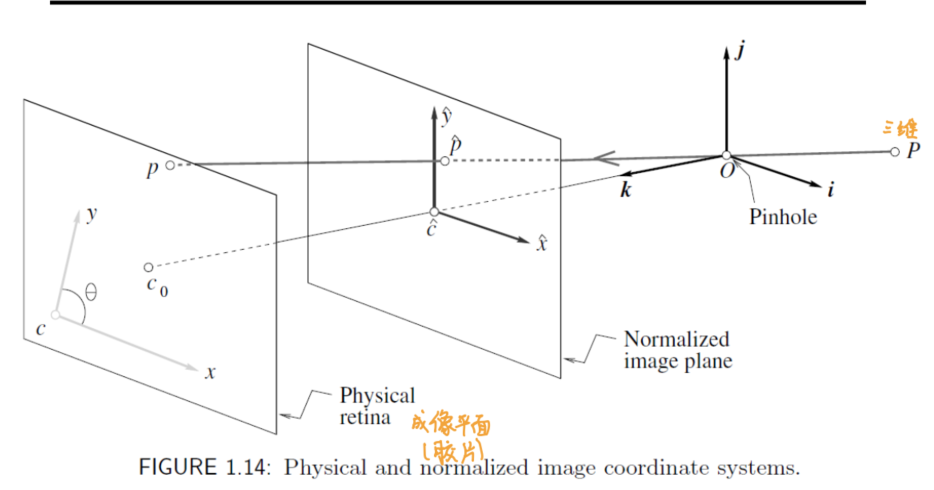
- 映射到成像平面(normalized image plane),相似三角形可解
- 映射到像素平面(physical retina), 通过对成像平面做出
缩放(比例)和平移(位置)操作-
- 当考虑误差时我们存在
角度的问题 -
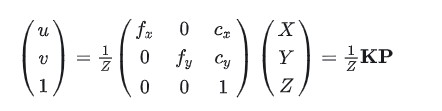
- 相机外参:世界坐标系到相机坐标系
-
Perspective/Pinhole Projection:
- For a point P in some fixed world coordinate , and its image p in the camera’s reference frame(normalized image plane), the projection equation is represented as:
- 从三维映射到二维平面(像素坐标系中,其以pixel units为单位,并且原点位于image的左上角!!)中去,其中M为相机矩阵with size of and
-
Shrinking the aperture
- 光圈越小成像越清晰,但更小时会产生衍射效应
- To control depth of field, 小光圈加大聚焦,但是减少亮度,需要z增加曝光
-
Adding a len
- len formula
- To influence the Field of View
- len flaws
- Vignetting(光晕):A photograph whose edges shade off gradually(遮光罩)
- Radial Distortion
- Spherical aberration(聚焦不到一个位置,散射光圈)
- Chromatic Aberration:Lens has different refractive indices for different wavelengths: causes color fringing(不同颜色聚焦不到一点,因为折射率不同)
-
Calibration
- Calibration
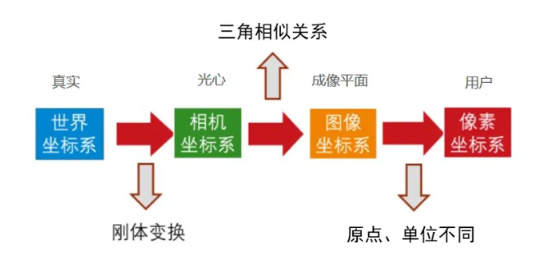
- Background: 使用single-view image去restore 3D structure是十分困难的,因为其中存在大量的歧义,因此我们需要multi-view images才能去进行重建,但此处存在着图片与图片之间的联系问题
- Goal: Calibration的目的在于坐标系之间的转换,从世界坐标系到图片坐标系,中间经过相机坐标系(标准坐标系),该过程与相机的内外参息息相关!!!
- Calibration matrix (实际上就是内参矩阵):
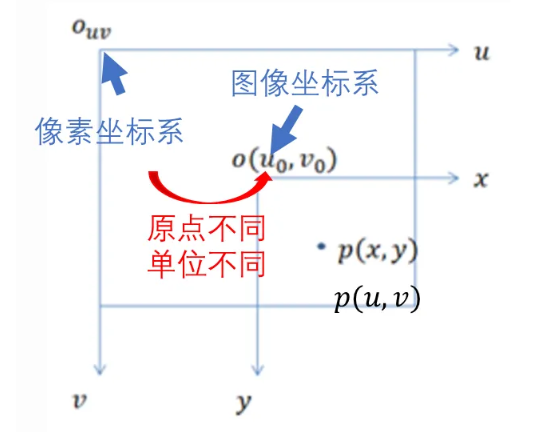
- 注意区分像素坐标系和图像坐标系
- 像素坐标系以图像左上角原点为原点,以pixel units为单位。
- 图像坐标系以图片的正中间为原点,仍以物理单位为单位
- Summary
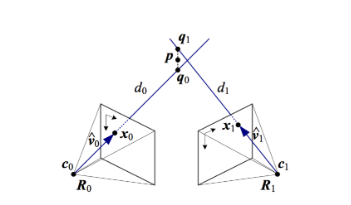
- 三角测定 Triangulation
- 在给定3D point在多个image中的投影,来求得该点在3D空间中的坐标
- 最小化
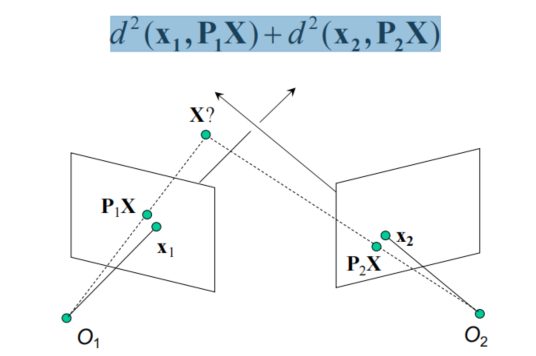
- 在给定3D point在多个image中的投影,来求得该点在3D空间中的坐标
Light
-
How to record light
- 从光信号转化为电信号(From analog to digital), recording by sensor array.
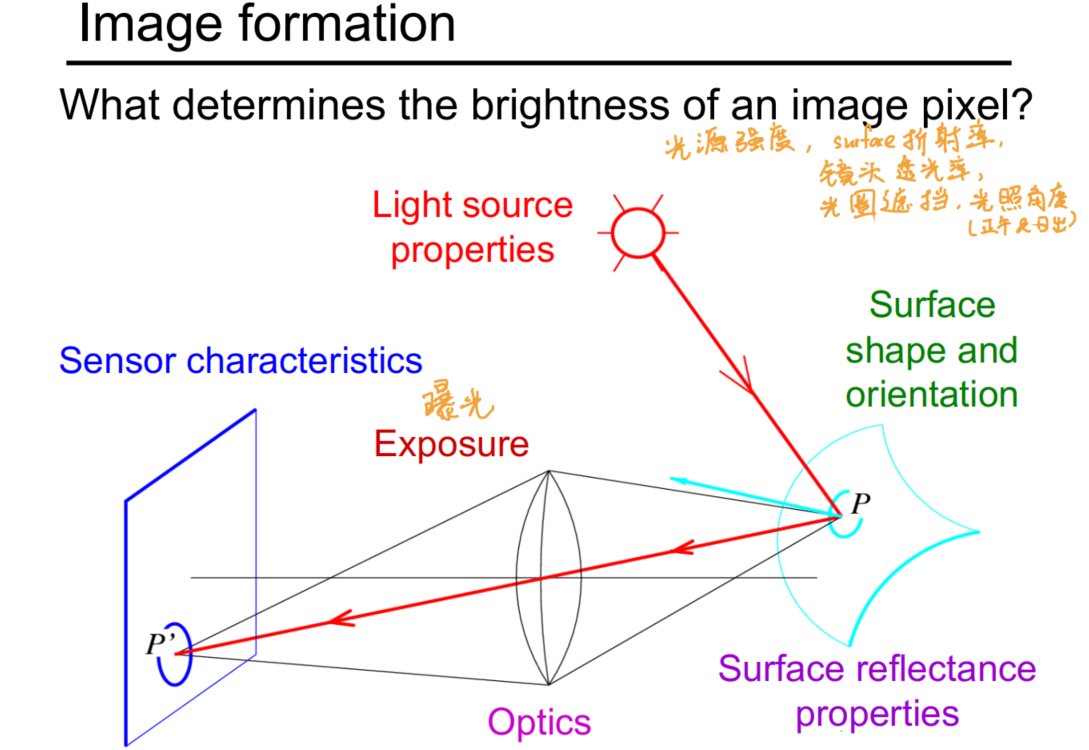
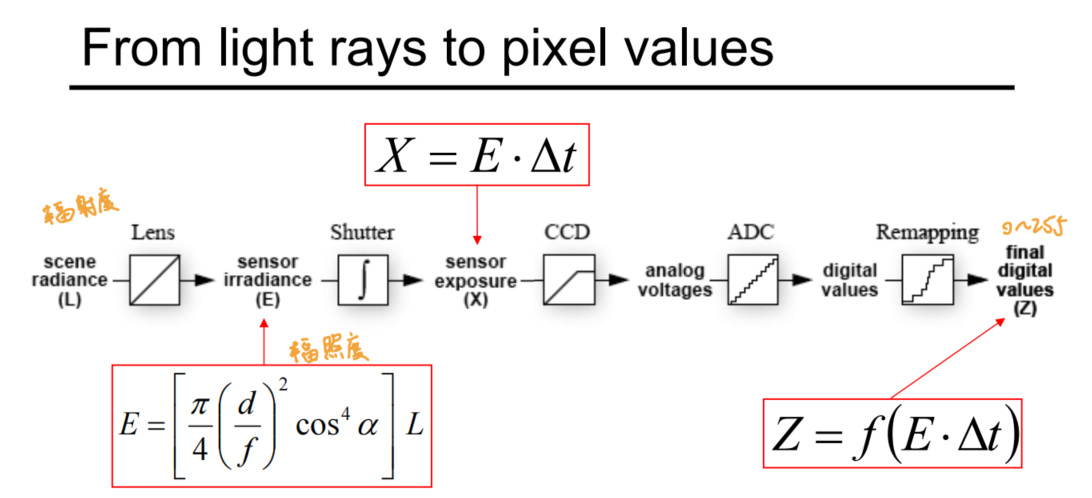
- 强度 Intensity:
- Intensity的大小取决于光照角度因为从斜角进入的光线少
- 反照率
- 直接光源
- surface normal法线
- 反射强度(reflect intensity)
- 辐射度和辐照度
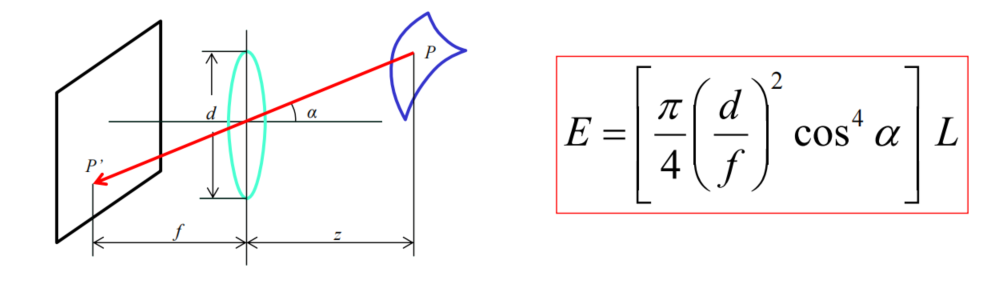
L: Radiance emitted from toward 辐射度- 光线携带的能量
E: Irradiance falling on from the lens 辐照度- 表面到达的能量
-
光子的表现
- Absorption 吸收
- Diffuse Reflection 漫反射(粗糙平面反射到各个方向equally,surface亮度取决于入射角)
- Specular Reflection 镜面反射
- Transparency 透明
- Refraction 折射
- Fluorescence 荧光(被光激发时释放能量)
- Subsurface scattering 次表面反射
- Phosphorescence 磷光(从激发态回到基态时释放能量)
- Interreflection 相互反射
-
Photometric stereo
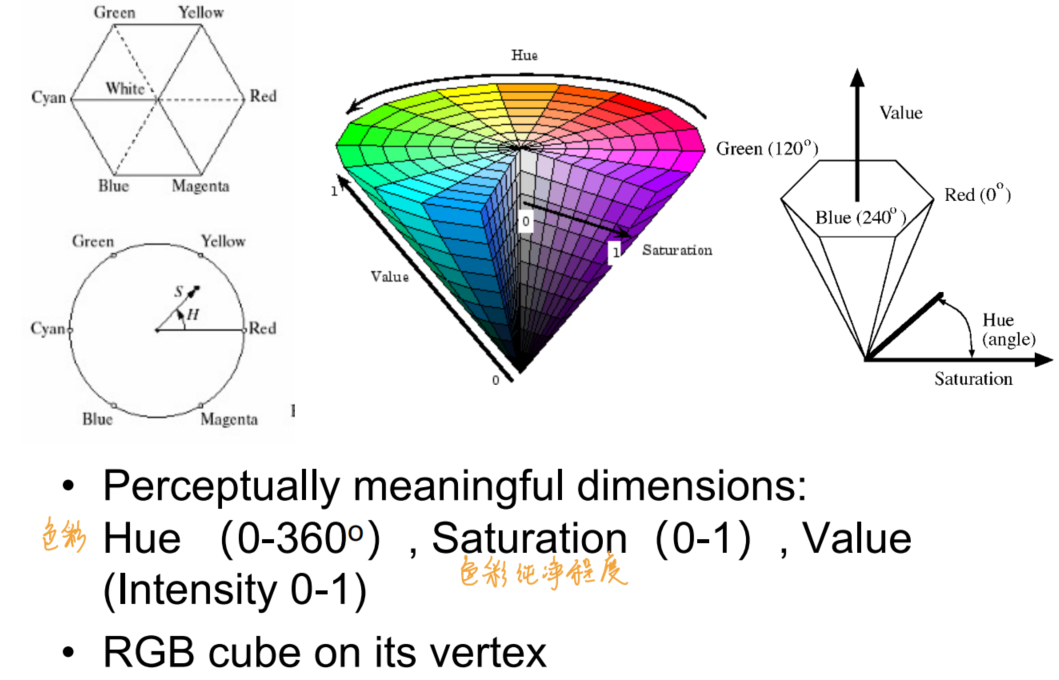
Color
- Standard color spaces
- def: Use a common set of primaries/color matching functions
- Linear color space
- RGB
- 单波长原色
- 适用于设备但不适用于感知
- RGB
- Non-linear color space
- HSV
- HSV
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.